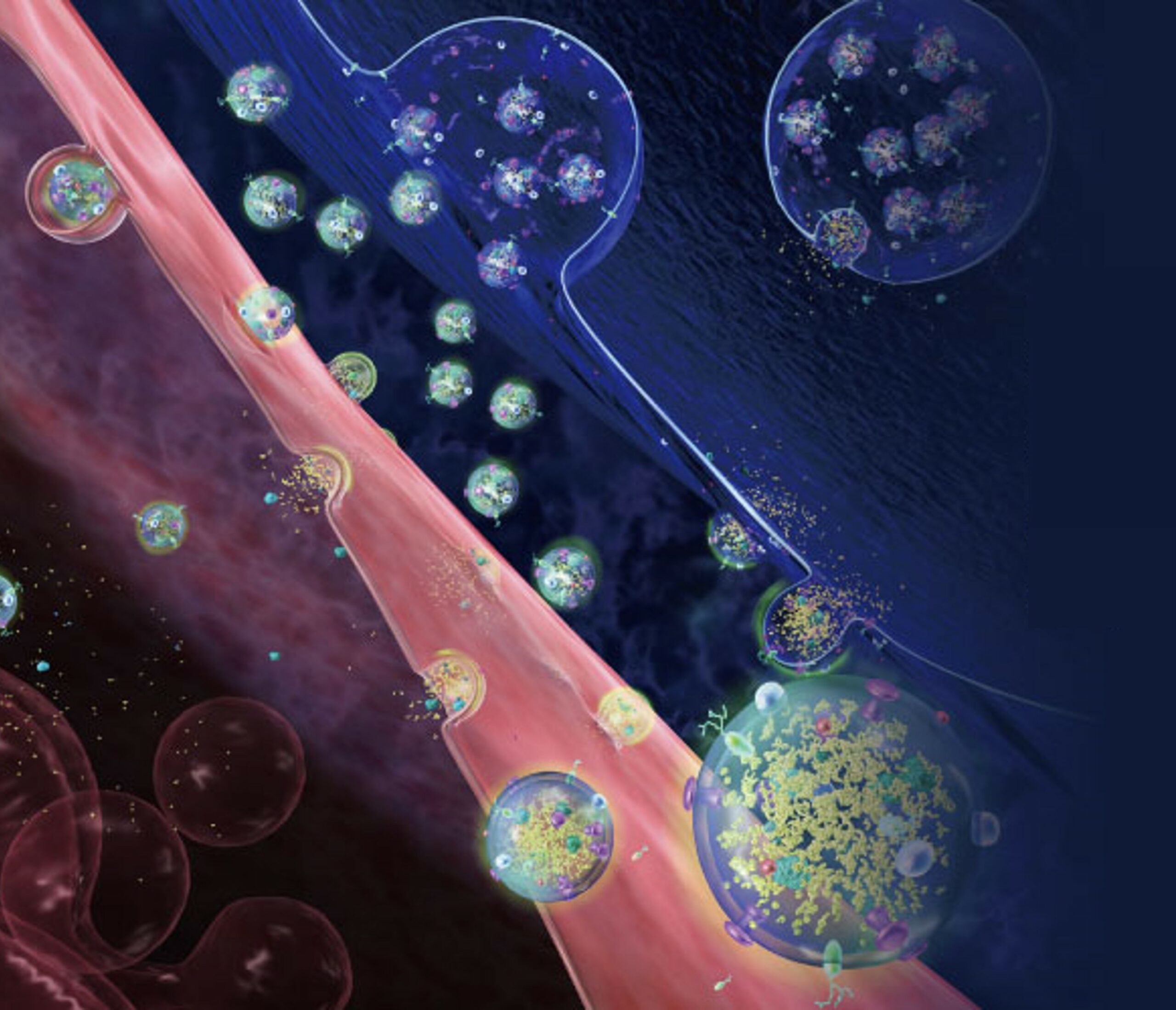
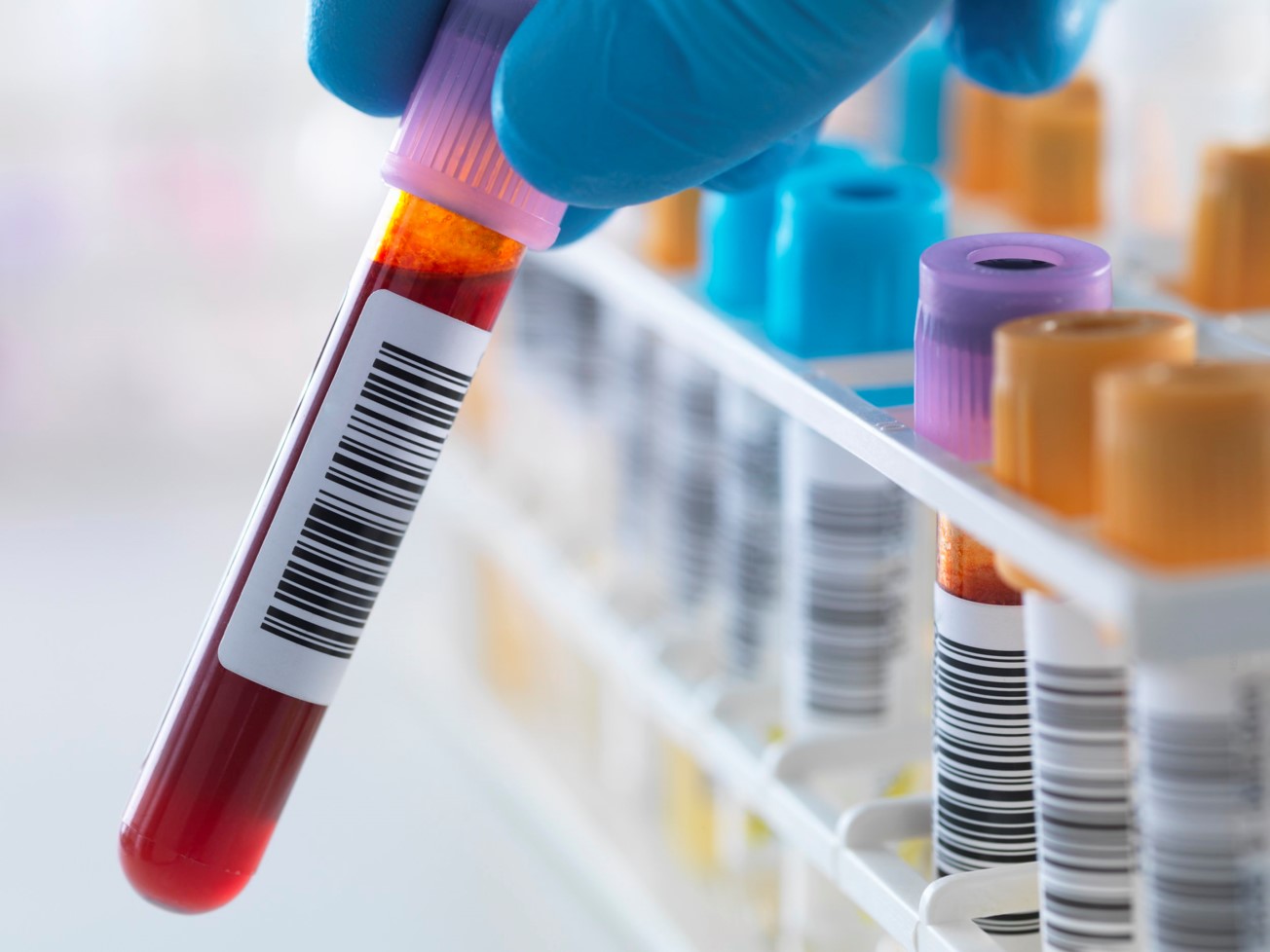
At Celer Diagnostics, we are passionate about bringing you the latest and most innovative solutions for cancer detection and treatment. One of these solutions is liquid biopsy, a blood test that can reveal vital information about your cancer without the need for invasive surgery.
What is liquid biopsy and how does it work?
Liquid biopsy is a blood test that can detect cancer cells or DNA fragments from a tumor that circulates in your bloodstream 1. By analyzing these biomarkers, liquid biopsy can help doctors diagnose more than 50 types of cancer, including advanced cancers, and match you to potential treatments based on the genetic changes in your tumor 2. Liquid biopsy can also be used for screening or early detection of cancer in high-risk patients or those with a personal or family history of cancer 3.
Liquid biopsy has several advantages over traditional tissue biopsy, which requires removing a sample of tissue from the tumor site. Liquid biopsy is:
- Simple: You only need to provide a blood sample, which can be done at any time and place.
- Non-invasive: You don’t need to undergo surgery, anesthesia, or hospitalization, which reduces the risk of complications and infections.
- Comprehensive: You can get a complete picture of your cancer, as a liquid biopsy can capture tumor heterogeneity and monitor changes over time.
- Personalized: You can get tailored treatment recommendations based on your tumor’s unique molecular profile.
What are some of the recent breakthroughs in liquid biopsy?
Liquid biopsy is a rapidly evolving field of research and innovation, with many exciting developments happening around the world. Some of the recent breakthroughs include:
- The FDA has expanded the approval of a liquid biopsy test, called FoundationOne Liquid CDx, that can identify more than 300 cancer-related genetic changes in DNA from tumor cells circulating in the blood [2]. This test can help match patients to targeted therapies and immunotherapies that are most likely to work for their specific type of cancer [2].
- A study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s annual meeting showed that a liquid biopsy test, called Galleri, could help speed up diagnosis and fast-track patients for treatment by detecting signs of cancer in people with symptoms [4]. The test could identify cancer-related DNA from more than 50 types of cancer and predict where in the body cancer originated [4].
- A research team at INTEGRA Biosciences has developed a novel liquid biopsy test that can detect prostate cancer with high accuracy and sensitivity by measuring the levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) in the blood [5]. The test could help combat prostate cancer by enabling early diagnosis and treatment [5].
How can Celer Diagnostics help you with liquid biopsy?
At Celer Diagnostics, we are proud to be part of this exciting field of innovation and we are committed to advancing liquid biopsy technology for better cancer care. We offer our own liquid biopsy test that can detect various types of cancers with high precision and reliability. Our test uses next-generation sequencing to analyze the DNA from tumor cells circulating in your blood and provide you with actionable insights into your cancer.
We invite you to learn more about our liquid biopsy test and how it can benefit you or your loved ones. Contact us today to schedule a consultation or request a quote.
1: Liquid Biopsy: What It Is & Procedure Details – Cleveland Clinic 2: FDA Approves Foundation Medicine’s Liquid Biopsy Test | FDA 3: Liquid Biopsy: A New Frontier in Cancer Detection | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: Blood Test Detects More Than 50 Types Of Cancer | ASCO: Novel Liquid Biopsy Test Detects Prostate Cancer With High Accuracy And Sensitivity | INTEGRA Biosciences
References
- my.clevelandclinic.org
- en.wikipedia.org
- pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- www.theguardian.com
- www.molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com